深入 Flask 源码了解 Blueprint
Blueprint
在使用 Blueprint 时,我一直很好奇它是如何工作的,因为在路由上的一些用法和 Flask 实在太像了。
翻阅 flask 文档中关于 Blueprint 的说明部分,了解 Blueprint 在做设计时的功能需求。
A blueprint in Flask is not a pluggable app because it is not actually an application
在使用过程中 Blueprint 和 Flask 使用很相似,如 url 路由的声明,异常的捕获等等,文档中却说
Blueprint 是可插拔式的, 但是它并不是一个 flask app。 这说明 Blueprint 的实现方法并不是继承 Flask
实现相同功能
Factor an application into a set of blueprints. Register a blueprint on an application at a URL prefix and/or subdomain. Register a blueprint multiple times on an application with different URL rules Provide template filters, static files, templates, and other utilities through blueprints. Register a blueprint on an application for any of these cases when initializing a Flask extension.
以上部分是关于 Blueprint 运用场景的说明。
- 一个 Flask 应用应该由多个
Blueprint组成 - 同一个
Blueprint下的 url 可以有共同的前缀 Blueprint可以由不同 url 注册多次Blueprint中可以提供资源文件的定位- 插件可以通过
Blueprint方式整合到Flask中
Blueprint实现的功能
- 与
Flask类一样可以指定资源位置 - 与
Flask一模一样的路由注册和管理,以及异常捕获,并且能在注册时指定 url 的前缀
这里不讨论资源的定位,主要是看 Blueprint 的实现,它是怎样与 Flask 联系的。
Blueprint 和 Flask 类之间的关系
我以为 Blueprint 会与 Flask之间联系会很大,毕竟直接参与到 Flask,
查看flask/blueprint.py后发现,实际上并不是这样的,中间涉及到 BlueprintSetupState 类。
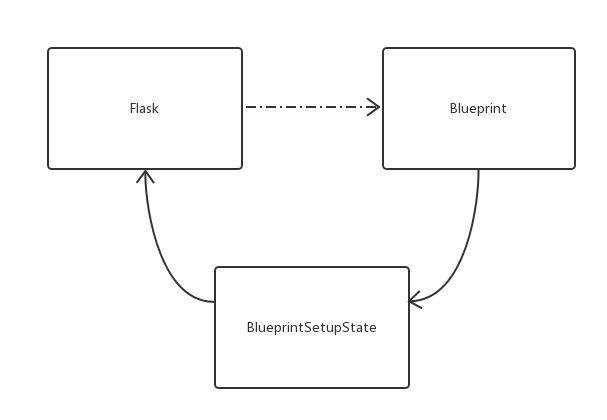
我的理解是 BlueprintSetupState是对 Flask 的一个代理。通过代理的方式使 Blueprint 和
Flask 解耦。在 Flask 中注册路由的时候,Blueprint上所有的操作直接由这个代理
落到了 Flask app 上。
以下是源码的解读部分。
源码说明
BlueprintSetupState
class BlueprintSetupState(object):
def __init__(self, blueprint, app, options, first_registration):
pass
def add_url_rule(self, rule, endpoint=None, view_func=None, **options):
'''
实现对 Flask app 的路由的代理
'''
pass
在 BlueprintSetupState 实例化时需要传入需要被代理的app 以及与操作对应的 Blueprint,
add_url_rule 代理了 Flask app 对于路由的操作
Blueprint 中的重要方法
class Blueprint(_PackageBoundObject):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
'''
这里少写了一些参数
'''
# ...
# blueprint 上的路由相关的函数都将添加到这里
# 添加的函数的参数统一为 BlueprintSetupState 的实例
# 因为这些操作都将会被 BlueprintSetupState 代理到 Flask 上
self.deferred_functions = []
# ...
def register(self, app, options, first_registration=False):
'''
blueprint 在 Flask 注册时调用,主要作用是将操作注册在Flask中
'''
# ...
state = self.make_setup_state(app)
for func in self.deferred_functions:
func(state)
# ...
def make_setup_state(self, app):
return BlueprintSetupState(self, app)
def record(self, func):
# ...
self.deferred_functions.append(func)
def record_once(self, func):
pass
def add_url_rule(self, rule, endpoint=None, view_func=None, **options):
self.record(lambda s:
s.add_url_rule(rule, endpoint, view_func, **options))
record 和 redcord_once 函数是向 deferred_function 添加函数, 这些函数都是以
BlueprintSetupState 实例为参数。 这两个方法将会被路由管理或者异常操作的函数调用了,
这里给出了 add_url_rule 方法作为例子。源码中可以看到添加的函数实质都是在调用 flask app
的路由操作。 blueprint 就是这样与 Flask 连接。
这里还有一个待解决的问题,blueprint 可插拔式的设计,只有在 app 中注册时才能使用。
Blueprint.register方法会解决这个问题。 register 中实例化了与 flask app 以及当前
Blueprint 实例绑定的 BlueprintSetupState 实例。 这个实例也会作为 record 等方法中添加
的函数的参数。 另外 Blueprint.register方法会在 app 注册蓝图时调用。
以下是注册蓝图的代码
class Flask(_PackageBoundObject):
# ...
def register_blueprint(self, blueprint, **options):
# ...
blueprint.register(self, options, first_registration)